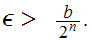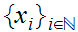 be a sequence in a Metric Space
be a sequence in a Metric Space
 .
We say the sequence converges to
.
We say the sequence converges to
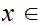
 ,
written
,
written
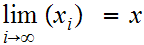 .
If for any
.
If for any
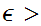 0 there
exists an
n
0 there
exists an
n such that
such that
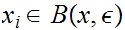 for
n
for
n .
.
19.1 Definition:
Let
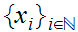 be a sequence in a Metric Space
be a sequence in a Metric Space
 .
We say the sequence converges to
.
We say the sequence converges to
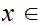
 ,
written
,
written
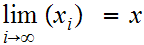 .
If for any
.
If for any
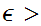 0 there
exists an
n
0 there
exists an
n such that
such that
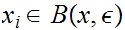 for
n
for
n .
.
19.2 Theorem:
Given Metric Spaces
 ,
, and a function
and a function
 ,
,
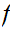 is continuous a point
is continuous a point

 if and only if for every
if and only if for every
 ,
,
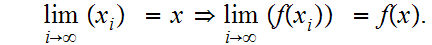 Note that this implies that
Note that this implies that
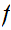 is is continuous at every point if and only if for every convergent sequence
is is continuous at every point if and only if for every convergent sequence

Proof:

Suppose
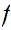 is continuous a point
is continuous a point

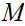 ,
then given any
,
then given any
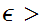 0
there is a
0
there is a
 0
such
that
0
such
that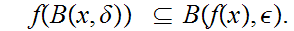
Since the sequence converges,
for
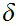 there
exists an
n
there
exists an
n such that
such that
 for
n
for
n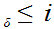 .
Hence, also,
.
Hence, also,
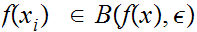 for
n
for
n
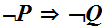
Conversly, suppose
 is not continuous at
is not continuous at
 ,
then there exits an
,
then there exits an
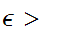 0.
Such that for
0.
Such that for
any
 0
we have
0
we have
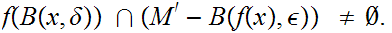
For every
 such
that
such
that
 and
and
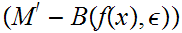 .
.
restated,
Use the Countable Axiom of Choice to choose
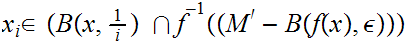
Clearly
 but
but

19.3 Definition:
Given a Metric Space
 ,
and a subset
,
and a subset
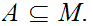 Define
Define
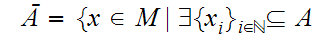 and
and
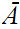 is called the closure of
is called the closure of
 .
.
19.4 Lemma:
 For
any
For
any
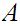 ,
,
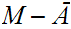 is open.
is open.
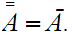 That is, the closure of the closure of
That is, the closure of the closure of
 is
the closure of
is
the closure of
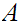 .
.
Proof:(To be turned in. Due April 6)
Solution:
1. Suppose that a given
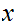 for any
for any
 0
we have
0
we have
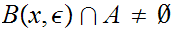 ,
,
then we could choose a sequnce in
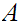 that converged to
that converged to
 ,then
,then

On the other had suppose that for any
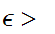 0
we have
0
we have
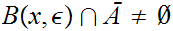
Let
 then we can find
then we can find
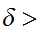 0
and a sequence
0
and a sequence
 such
that
such
that
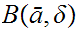
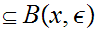 ,
,
 and
hence
and
hence
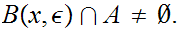
2. By definition

 Next suppose
Next suppose
 , where
, where
 .
For each
.
For each
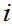 choose
choose
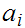 such that
such that
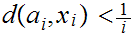 .
One checks that
.
One checks that
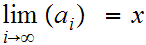
19.5 Definition:
We call a subset
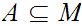 dense if
dense if
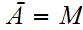 .
.
Example:
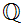 is dense in
is dense in
 .
.
19.6 Theorem:
Given Metric Spaces
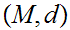 ,
,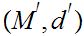 , continuous functions,
, continuous functions,
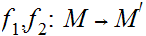 , and a dense subset
, and a dense subset
 ,
if
,
if
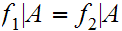 then
then
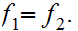
Proof:
Suppose
 and
and is
such
that
is
such
that .
.
then
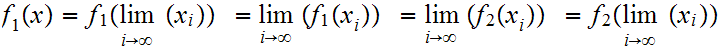
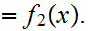
19.7 Example:
Let
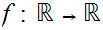 be continuous and suppose
be continuous and suppose
 0
for all
0
for all
 ,
then
,
then
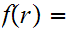 0
for all
0
for all
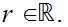
 is said to be additive if
is said to be additive if
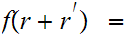
 for all
for all
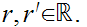 If
If
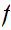 is also continuous then
is also continuous then
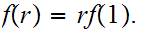
Proof of 2: (To be turned in. Due April 6)
Hint:
Prove it first for
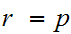 and
and
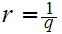 with
with

Next for
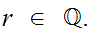
Solution:
Given
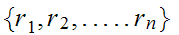 A
simple induction argument shows that
A
simple induction argument shows that
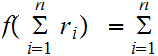
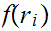
Hence
 We can now apply 1. since the function
We can now apply 1. since the function
 is zero on
is zero on
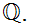
19.8 Bonus Question:
Given
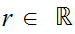 ,
we call a function
,
we call a function
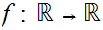 bounded near
bounded near
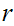 .
if there exists
.
if there exists
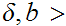 0 such that
0 such that
 .
.
Note that this does not say that for any
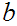 there
exists a
there
exists a
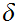 .
.
Prove that if
 is
additive, and there exists some
is
additive, and there exists some
 such that
such that
 is bounded
near
is bounded
near 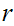 ,
then
,
then
 is continous everywhere and hence
is continous everywhere and hence

Solution:
If
 is bounded near one point then by linerarity it is bounded everywhere.
is bounded near one point then by linerarity it is bounded everywhere.
If
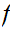 is bounded
near
is bounded
near 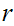 then it is continuous
at
then it is continuous
at 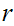 .
.
Suppose there exists
 0 such that
0 such that
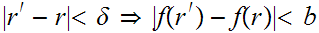 .
Suppose
.
Suppose
 . Let
. Let
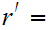 2
2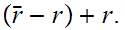
Then
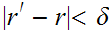 and hence
and hence
 2
2 2
2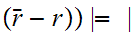 2
2
or

and by induction
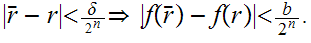
Finally, given
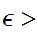 0 choose n such that
0 choose n such that