C References
Assignments
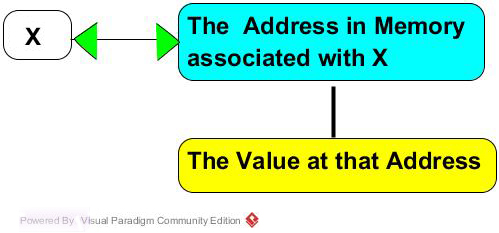
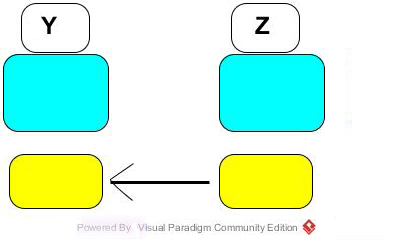
y=z :Take the value found at the address associated with z and place it in memory location whose address is assocated with y.
-------------------------------------------
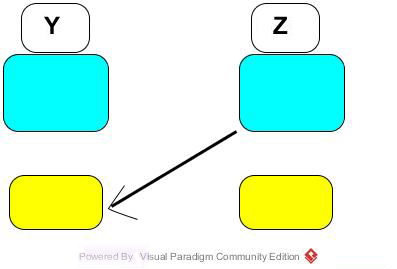
y=&z :Take the address associated with z and place it in memory location whose address is assocated with y.
-------------------------------------------
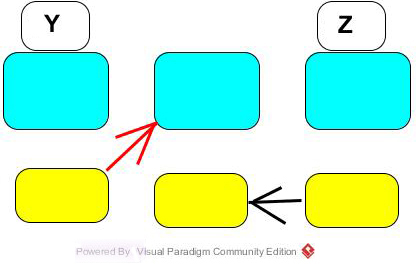
*y=z :Take the value found at the address associated with z and place it in the memory location whose address is found in
the memory location whose address is assocated with y.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
printf("###########################\nint pointers and addresses\n###########################\n");
int x=5,y=6,z=7;
int *p;
printf("the address of p %p\n", &p);
printf("the address p is pointing to is %p\n", p);
p=&x;
printf("the address p is pointing to is now %p\n", p);
printf("the value p is pointing to is now %i\n", *p);
x=y;
printf("the address p is pointing to is now %p\n", p);
printf("the value p is pointing to is now %i\n", *p);
p=&y;
printf("the address p is pointing to is now %p\n", p);
printf("the value p is pointing to is now %i\n", *p);
*p=z;
printf("the value of y is now %i\n", y);
printf("the value p is pointing to is now %i\n", *p);
printf("\n###########################\nchar pointers and addresses\n###########################\n");
char the_string[]="just a string.";
printf("the_string address = %p\n", the_string);
printf("and as the address of &the_string[0] = %p\n", &the_string[0]);
printf("the_string itself is \"%s\"\n",the_string);
printf("*the_string points the first character which is %c\n",*the_string);
printf("the_string[3] = %c\n", the_string[3]);
return 0;
}
struct
typedef




