FIXATION
DISPARITY
1. Definition
a. purpose
b. indicator of fast vergence activity
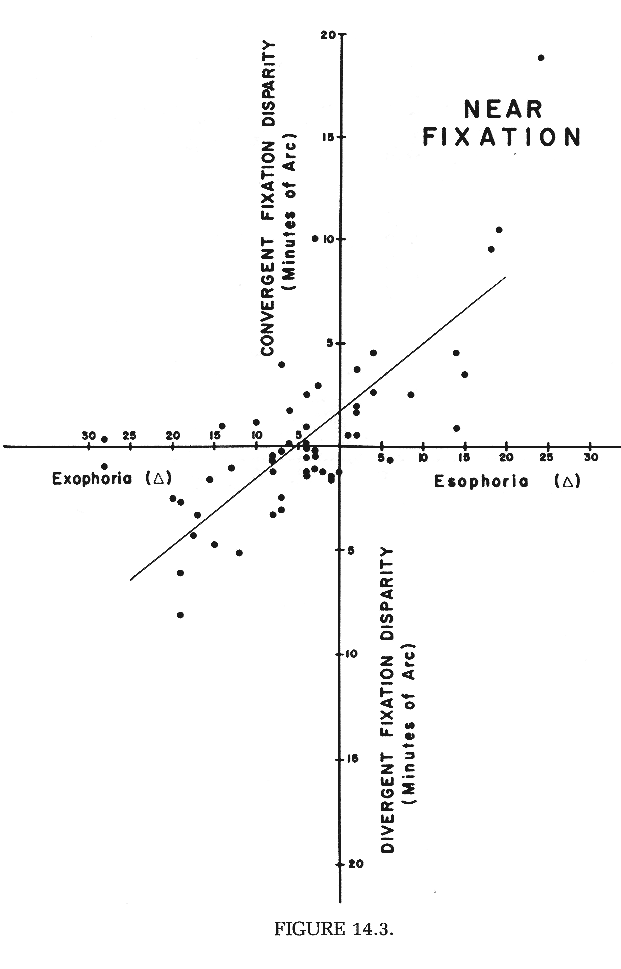
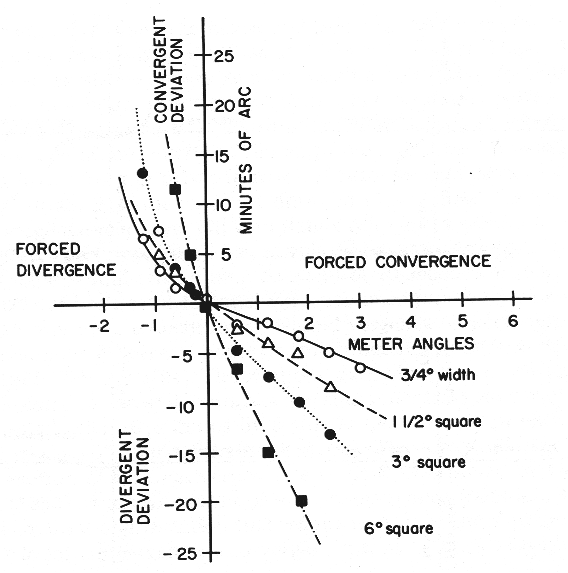
i. exophoria: linear relationship, fixation
disparity & positive fusional vergence
ii. esophoria: linear relationship, fixation disparity
& negative fusional vergence for small esophoria,
non-linear for moderate, high esophoria; i.e. more fixation
disparity required for a given level of esophoria than in
exophoria; i.e. negative fast vergence system is less
efficient!
c. not the same as the heterophoria
i. associated versus dissociated conditions
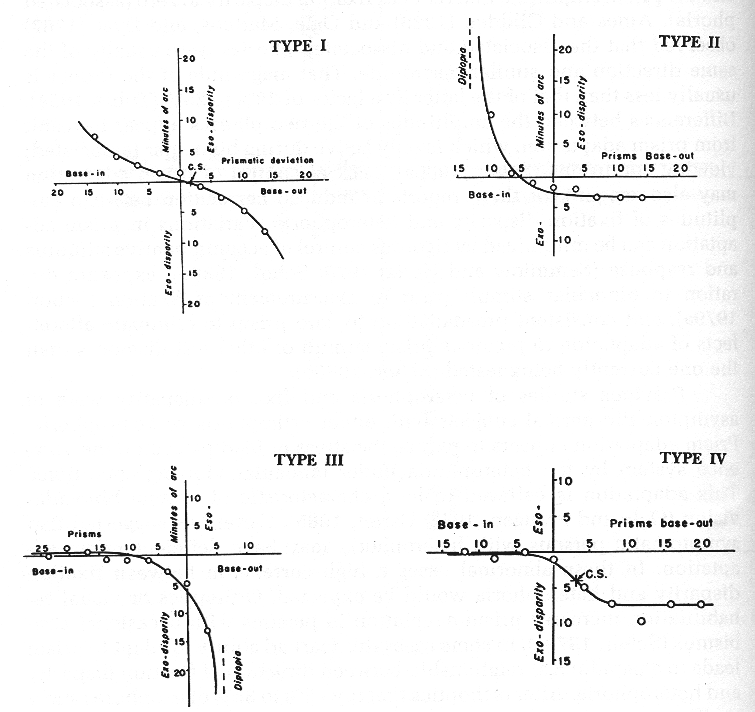
2. Fundamental variables of the forced vergence fixation disparity
curve:
a. y-intercept - the habitual actual fixation disparity
(0 prism)
b. x-intercept - the associated phoria (prism to neutralization
of fixation disparity)
c. slope - measured between 3 base-in & 3 base-out
d. type - I - IV
3. Signs / symptoms / important facts
a. y-intercept - 10' arc exo, almost any eso FD
b. x-intercept - prism correction
c. slope - > 1.0 (i.e. 1' arc / 1 prism diopter)
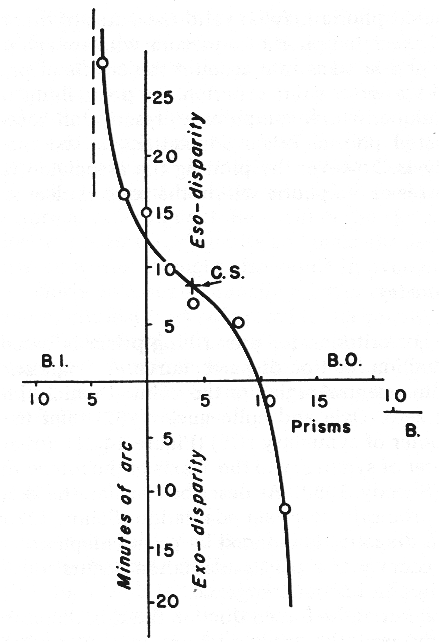
a steep Type I curve
slope = Dy/Dx
slope = 9/7 = 1.3
4. Clinical use of fixation disparity
a. prism Rx determination
i. determine need for prism correction
ii. Rx 50% of the associated phoria [associated phoria =
prism to neutralize the fixation disparity; or, the amount of
prism that makes the fixation disparity 0].
b. monitor effects of vision therapy
i. increases sensitivity of disparity detectors
ii. increases level of prism adaptation (slow vergence
adaptation)
STEREOPSIS
"barometer of binocular vision"
1. Clinical factors affecting stereoacuity
a. strabismus
b. amblyopia
c. blur / contrast
1. visual acuity / refractive error
2. accommodative dysfunction
d. fixation disparity
1. not heterophoria directly
2. anisophoria
e. suppression
f. aniseikonia
2. Clinical stereopsis tests
a. local, non threshold tests
1. Stereo fly - 40 sec
2. Randot - 20 sec
b. global
1. Random Dot E
3. Expected - 40 sec (local)
SUPPRESSION
1. Loss of sensitivity
a. facultative
b. obligatory
2. Effect on binocularity
a. stereopsis
b. fixation disparity measurements
3. Presentation
a. strabismus - constant, unilateral, regional
b. non-strabismus - intermittent, alternating (then
unilateral), central (foveal)
 i. exophoria: linear relationship, fixation disparity & positive fusional vergence
i. exophoria: linear relationship, fixation disparity & positive fusional vergence