Flat-Space Motion in 1D
Motion may be described using displacement x, time t, and simultaneity referenced to a map frame, with time on traveling clocks (τ) inferred from the metric relation|
|
|
|
|
|
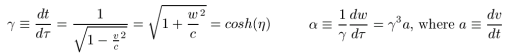
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
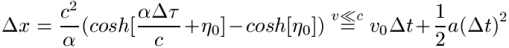
story:
#1
pzzlrs:
#1,2 q&a:
soon..
links:
CALC
dynmcs
3Dkine
extra:
recent
ancient
| Content Modernization: 1FrameViews: ... |